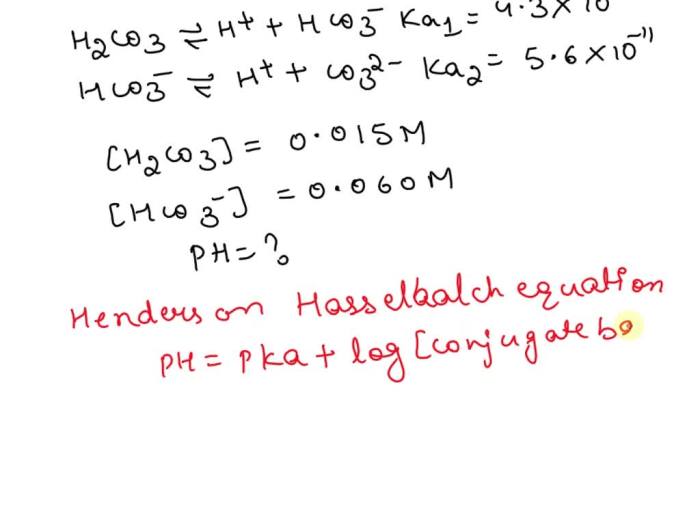Complete the ka1 expression for h2co3 in an aqueous solution – Complete the Ka1 expression for H2CO3 in aqueous solution, a topic of significant importance in chemistry, provides a fundamental understanding of acid-base equilibria and the behavior of carbonic acid in various systems. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of Ka1, its derivation, and applications, while exploring the factors influencing its value and the experimental techniques used to determine it.
Delving deeper into the intricacies of Ka1, we uncover its role in calculating pH, determining ion concentrations, and understanding the behavior of carbonic acid in biological systems. The experimental determination of Ka1, employing various spectroscopic techniques, further enhances our comprehension of this crucial equilibrium constant.
Understanding the Ka1 Expression for H2CO3 in Aqueous Solution

The Ka1 expression for H2CO3 in aqueous solution is a mathematical equation that describes the equilibrium constant for the first dissociation of carbonic acid (H2CO3) into hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). The Ka1 value is a measure of the acidity of H2CO3 and is important in understanding the behavior of carbonic acid in various chemical and biological systems.
Chemical Equation for the Dissociation of H2CO3
The chemical equation for the dissociation of H2CO3 in water is as follows:
H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + HCO3-(aq)
The equilibrium constant, Ka1, for this reaction is defined as the ratio of the concentrations of the products (H3O+ and HCO3-) to the concentration of the reactant (H2CO3) at equilibrium.
Derivation of the Ka1 Expression, Complete the ka1 expression for h2co3 in an aqueous solution
The Ka1 expression can be derived using the law of mass action. The law of mass action states that the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction is equal to the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the reactants, each raised to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
For the dissociation of H2CO3, the Ka1 expression is:
Ka1 = [H3O+][HCO3-] / [H2CO3]
where [H3O+], [HCO3-], and [H2CO3] represent the equilibrium concentrations of the respective species.
Q&A: Complete The Ka1 Expression For H2co3 In An Aqueous Solution
What is the significance of the Ka1 expression?
The Ka1 expression quantifies the extent of dissociation of H2CO3 in aqueous solution, providing insights into the strength of the acid and the equilibrium concentrations of its ions.
How does temperature affect the Ka1 value?
Temperature generally has a negative effect on the Ka1 value, indicating that the dissociation of H2CO3 decreases with increasing temperature.
What experimental techniques are used to determine the Ka1 value?
Spectroscopic techniques, such as UV-Vis spectrophotometry and NMR spectroscopy, are commonly employed to determine the Ka1 value by measuring the absorbance or chemical shifts associated with the dissociation of H2CO3.