Introducing the Amendment Worksheet Bill of Rights 1-10, a comprehensive guide that delves into the cornerstone of American liberties. This meticulously crafted resource provides an in-depth analysis of the first ten amendments to the US Constitution, exploring their historical significance, legal implications, and enduring impact on society.
Through a series of engaging sections, we will dissect each amendment, examining its purpose, scope, and the landmark cases that have shaped its interpretation. From the fundamental freedoms of speech and religion to the right to bear arms and the protections against unreasonable searches and seizures, this worksheet offers a comprehensive understanding of the Bill of Rights.
1. Amendment Worksheet Bill of Rights 1-10
An Introduction
The Bill of Rights, comprising the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution, serves as a fundamental framework for protecting individual liberties and rights against government overreach. It was adopted in 1791 as a response to concerns that the original Constitution lacked sufficient safeguards for personal freedoms.
An Amendment Worksheet provides a structured and comprehensive resource for understanding the Bill of Rights. It typically includes a summary of each amendment, relevant historical context, and case studies or examples that illustrate its application in practice.
2. Understanding the First Amendment
The First Amendment protects five essential freedoms: religion, speech, press, assembly, and petition. It establishes the separation of church and state, ensuring that individuals are free to practice their religion without government interference.
Freedom of speech and expression are crucial for a democratic society, allowing individuals to express their views and challenge prevailing opinions. Landmark cases such as Tinker v. Des Moines(1969) and Citizens United v. FEC(2010) have shaped the interpretation and application of the First Amendment.
3. Exploring the Second Amendment
The Second Amendment guarantees the right of individuals to keep and bear arms. This right is rooted in the historical context of self-defense and the need for a militia to protect the country. However, the scope and interpretation of the Second Amendment have been subject to ongoing debate.
Comparative analysis of gun control laws in different countries provides insights into the varying approaches to balancing the right to bear arms with public safety concerns.
4. Analyzing the Third Amendment

The Third Amendment prohibits the quartering of soldiers in private homes without the owner’s consent. This amendment reflects the historical concerns about the British practice of billeting soldiers in civilian homes during the American Revolution.
While the Third Amendment may seem outdated in modern society, it serves as a reminder of the importance of protecting private property and the sanctity of the home against government intrusion.
5. Understanding the Fourth Amendment

The Fourth Amendment protects against unreasonable searches and seizures by requiring law enforcement to obtain a warrant based on probable cause. It aims to balance the government’s need for evidence with the individual’s right to privacy.
The exclusionary rule, which prohibits the use of evidence obtained in violation of the Fourth Amendment, has been a significant tool in safeguarding individual rights.
6. Exploring the Fifth Amendment
The Fifth Amendment guarantees due process of law and protects against self-incrimination. Due process requires that individuals are treated fairly and according to established legal procedures.
The Miranda rights, which inform suspects of their right to remain silent and to an attorney, are essential for ensuring that individuals are not coerced into confessing to crimes.
7. Analyzing the Sixth Amendment
The Sixth Amendment safeguards the rights of the accused in criminal trials, including the right to counsel, a fair and impartial jury, and the right to confront witnesses.
The application of the Sixth Amendment has been instrumental in ensuring the fairness and integrity of the criminal justice system.
8. Understanding the Seventh Amendment
The Seventh Amendment guarantees the right to a jury trial in civil cases involving more than $20. This right ensures that disputes are resolved by a jury of peers, rather than solely by a judge.
The Seventh Amendment plays a crucial role in preserving the democratic principles of due process and the right to a fair trial.
9. Exploring the Eighth Amendment
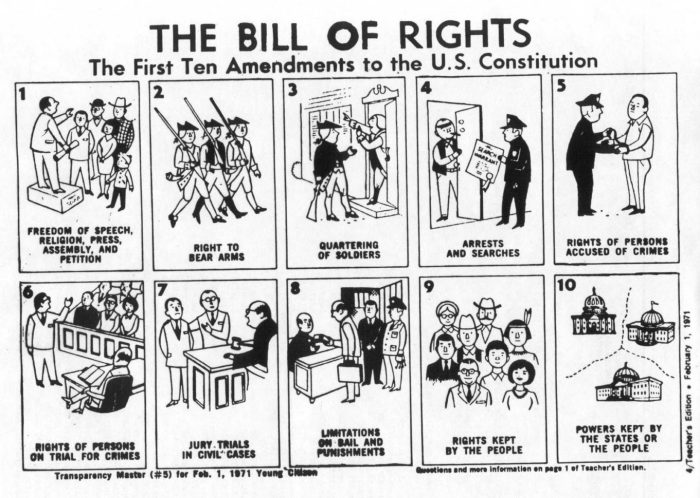
The Eighth Amendment prohibits excessive bail and cruel and unusual punishment. It seeks to prevent the government from imposing excessive or disproportionate penalties that violate human dignity.
The application of the Eighth Amendment has been particularly relevant in capital punishment cases, where it has been used to challenge the constitutionality of certain methods of execution.
10. Analyzing the Ninth and Tenth Amendments

The Ninth Amendment recognizes that there are rights that are not explicitly enumerated in the Constitution. The Tenth Amendment reserves powers not delegated to the federal government to the states or the people.
These amendments play a significant role in defining the balance of power between the federal and state governments, as well as protecting unenumerated rights.
FAQ Corner: Amendment Worksheet Bill Of Rights 1-10
What is the purpose of the Bill of Rights?
The Bill of Rights, comprising the first ten amendments to the US Constitution, establishes fundamental rights and freedoms for individuals, protecting them from government overreach.
How does the First Amendment protect freedom of speech?
The First Amendment guarantees the right to express oneself freely, including through speech, press, assembly, and religion, with certain limitations to protect public order and national security.
What are the key provisions of the Second Amendment?
The Second Amendment secures the right of individuals to keep and bear arms for self-defense and other lawful purposes, subject to reasonable regulations.